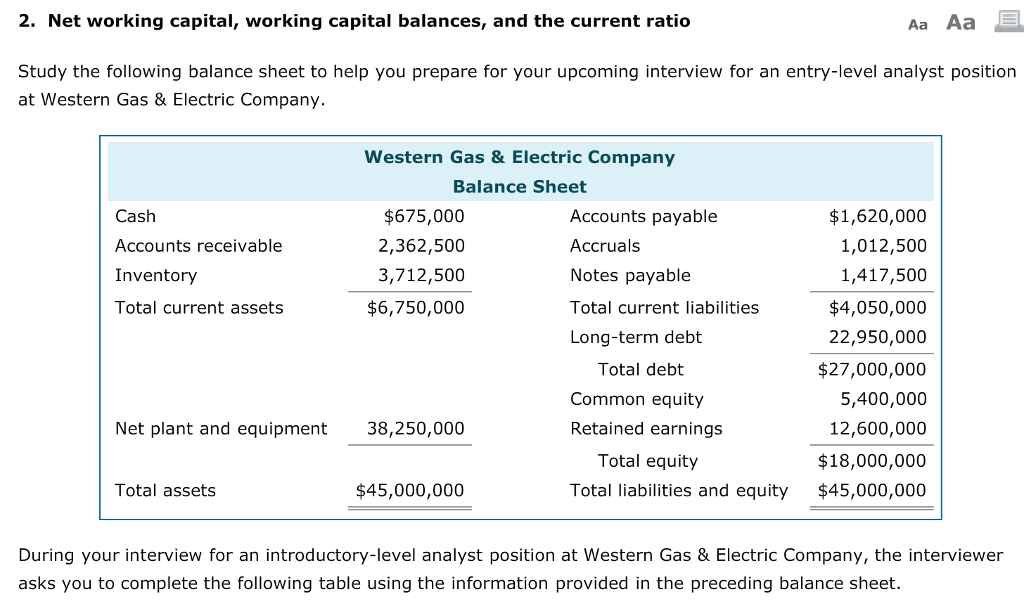
First Class Info About Net Working Capital Balance Sheet Statement Of Partnership Income
($ 2,000,000) in scenario b, the seller delivered a net working capital that is lower than the peg.
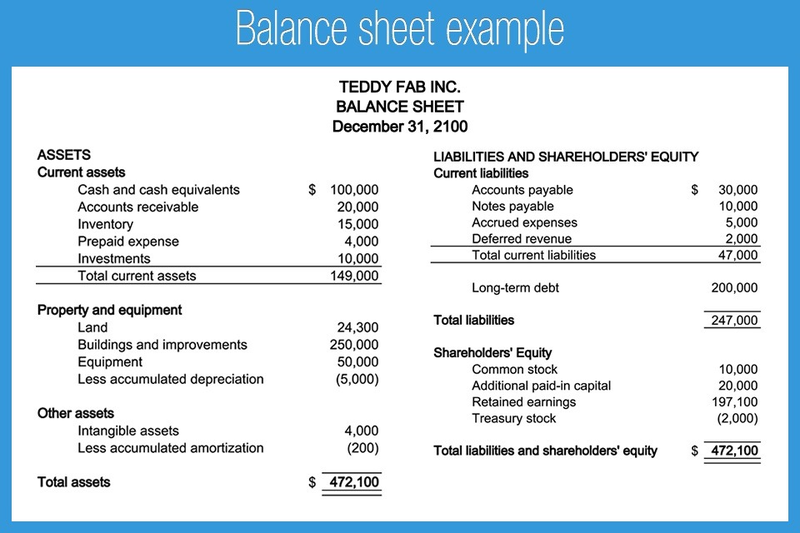
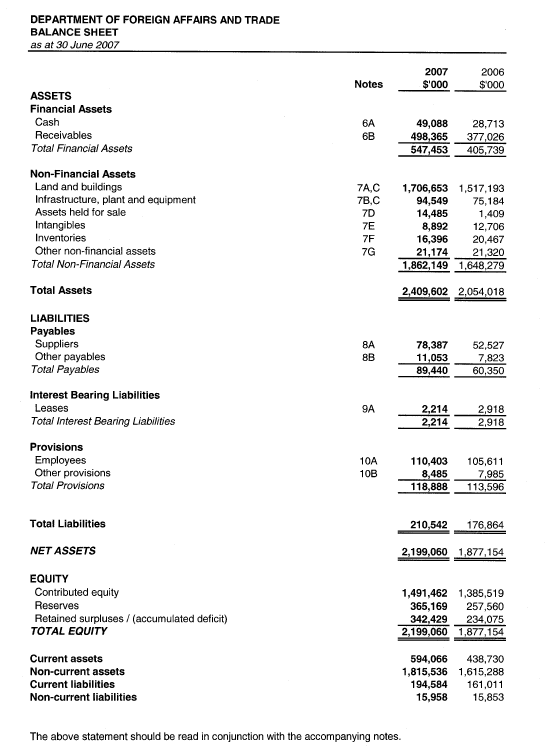
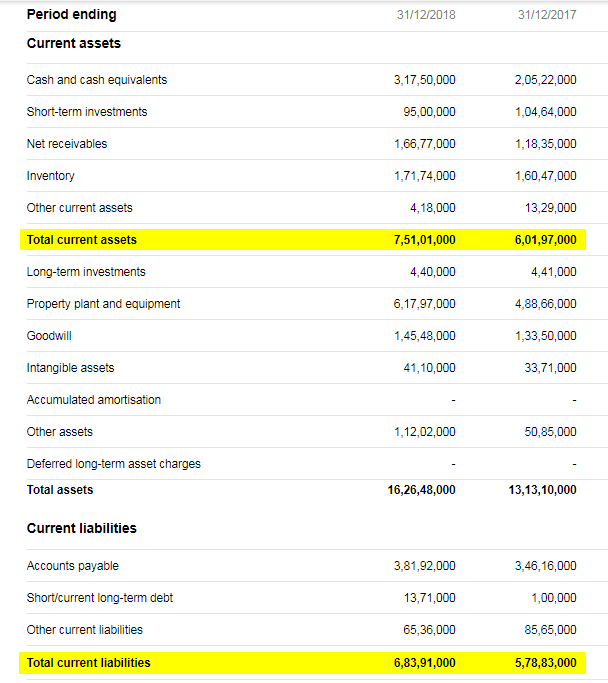
Net working capital balance sheet. A company’s balance sheet is a snapshot in time. June 24, 2021 with access to a company’s balance sheet, net working capital can be calculated simply by subtracting current liabilities from current assets. Simply put, it indicates your liquidity or ability to pay your bills.
Under sales and cost of goods sold, lay out the relevant balance sheet accounts. It is calculated as the difference between the total current assets and the total current liabilities. It is calculated as the difference between current assets and liabilities on the balance sheet.
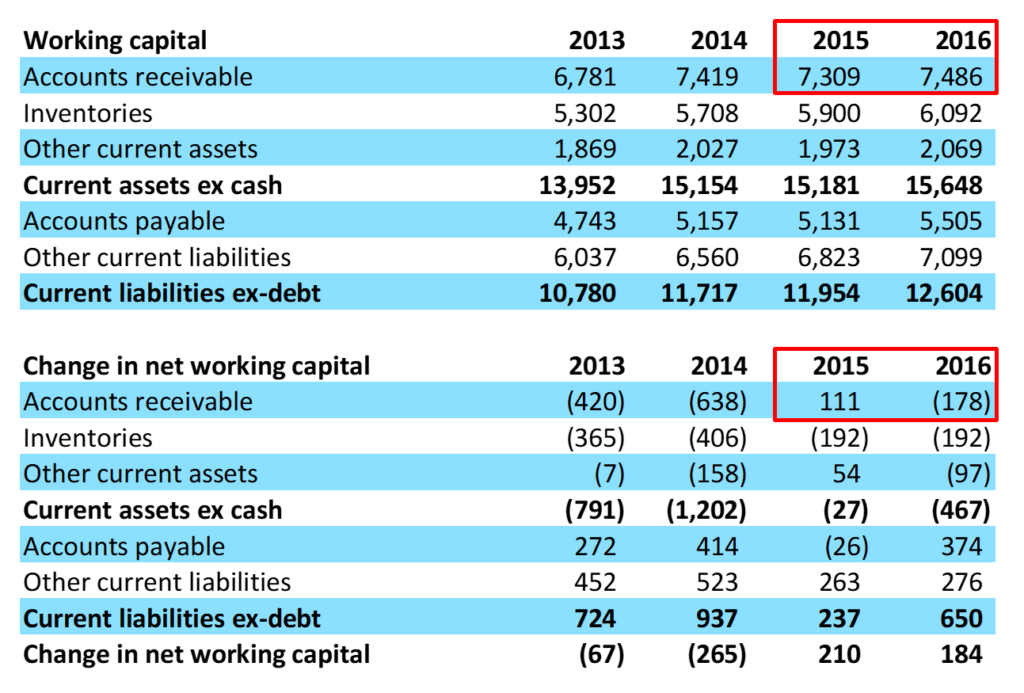
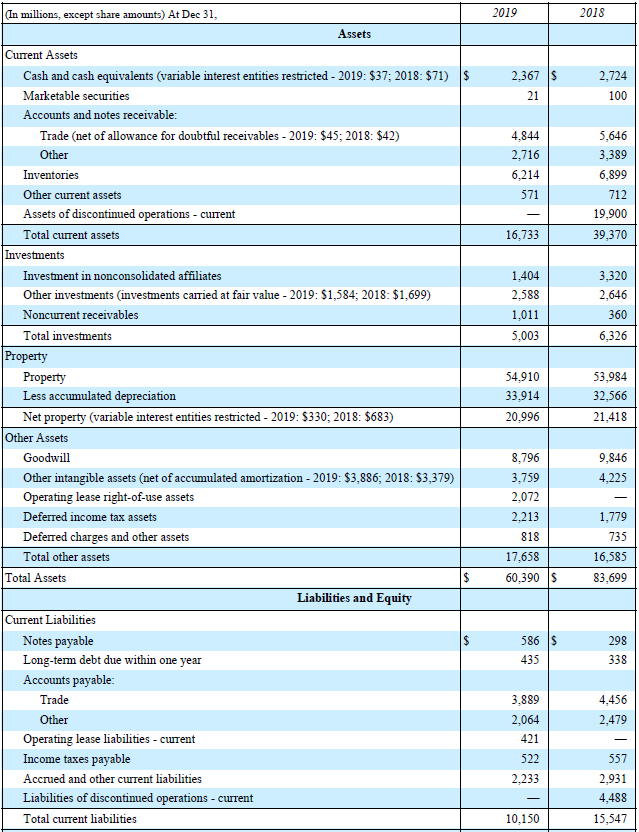
Working capital, also known as net working capital (nwc), is the difference between a company’s current assets —such as cash, accounts. To calculate net working capital, you must begin by looking at the company’s balance sheet. These are the line items from the balance sheet included in the net working capital calculation:
The net working capital (nwc) metric is a measure of liquidity that helps determine whether a company can pay off its current liabilities with its current assets on hand. What is working capital? Net working capital (nwc) is the difference between a company’s current assets (net of cash) and current liabilities (net of debt) on its balance sheet.
At the very top of the working capital schedule, reference sales and cost of goods sold from the income. Key takeaways net working capital is a measure of a company's liquidity. Working capital is calculated by subtracting current liabilities from current assets, as listed on the company’s balance sheet.
A high net working capital is not always a good thing. Total liabilities divided by shareholder equity. Current assets include cash, accounts receivable and inventory.
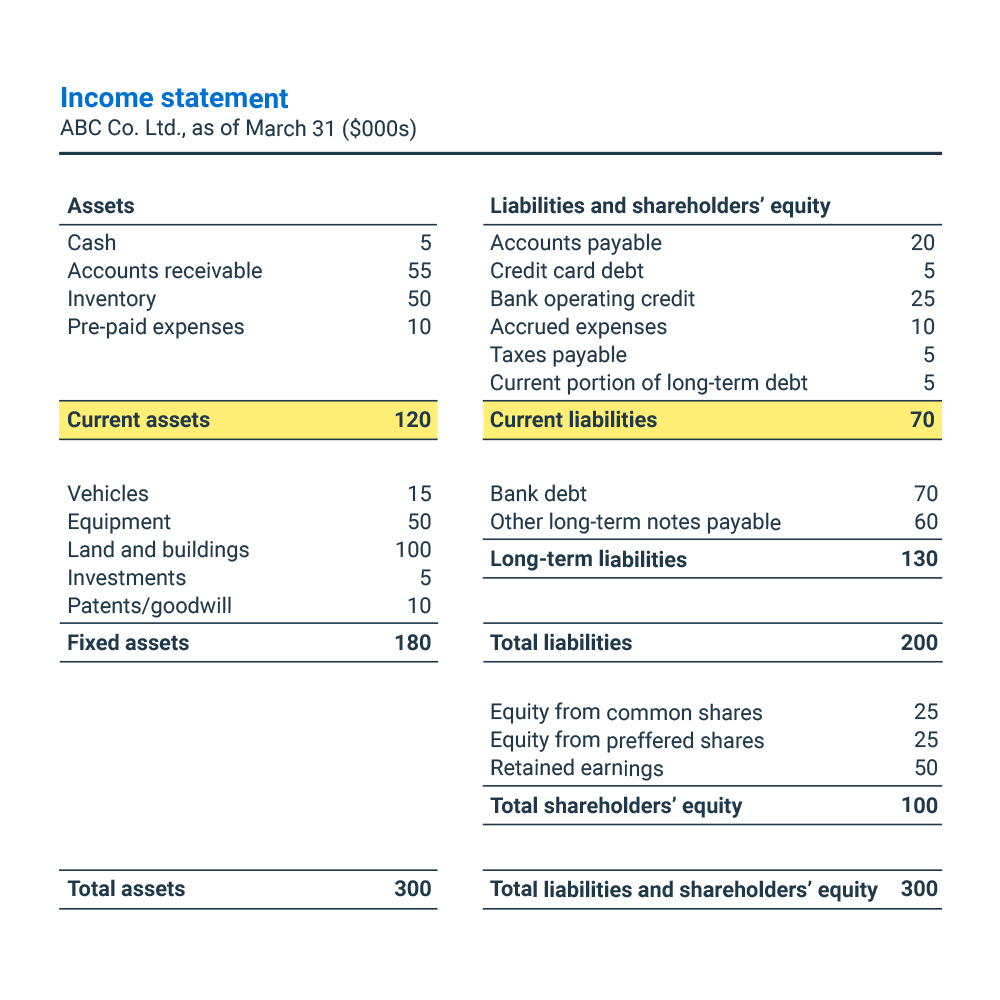
How to calculate net working capital? A balance sheet is a financial statement that reports a company's assets, liabilities and shareholder equity at a specific point in time. Net working capital considers items specified in the balance sheet and is the difference between a company's current assets and current liabilities.
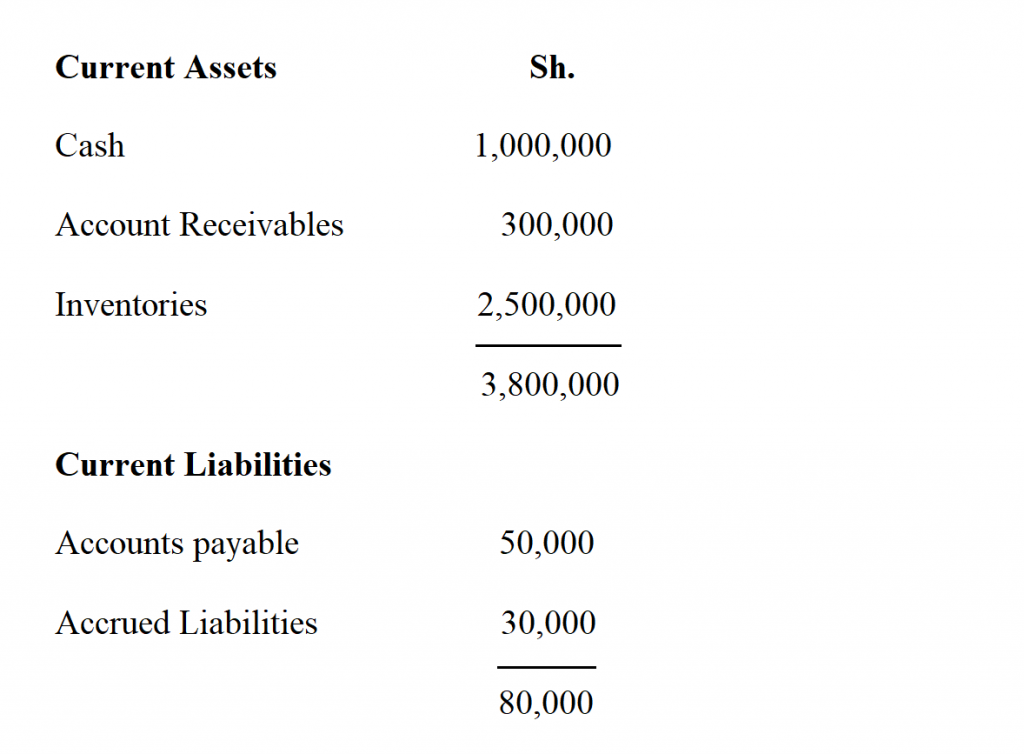
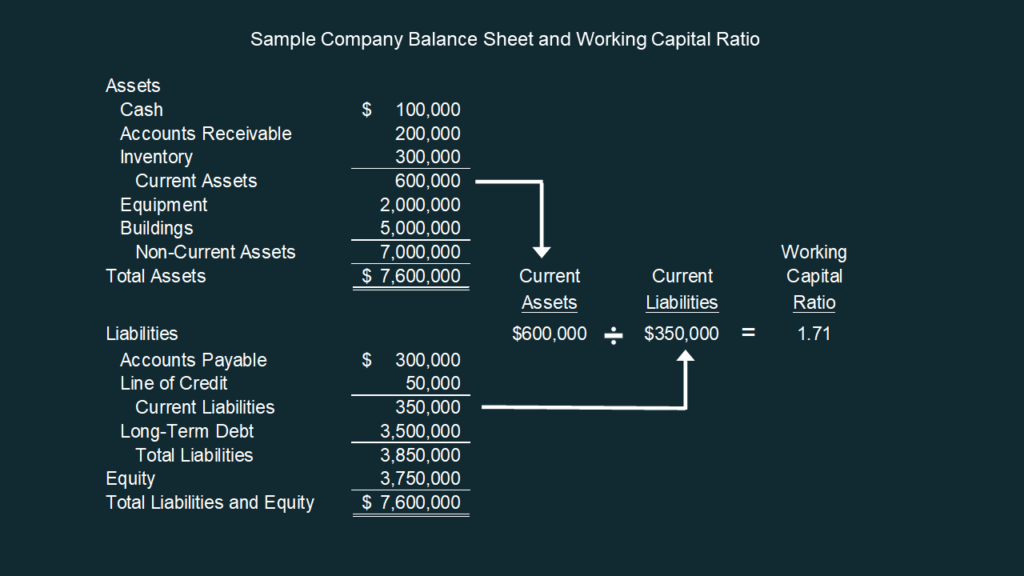
Current ratio here’s an example: Net working capital at close. As a general rule, the more current assets a company has on its balance sheet relative to its current liabilities, the lower its liquidity risk (and the better off it’ll be).
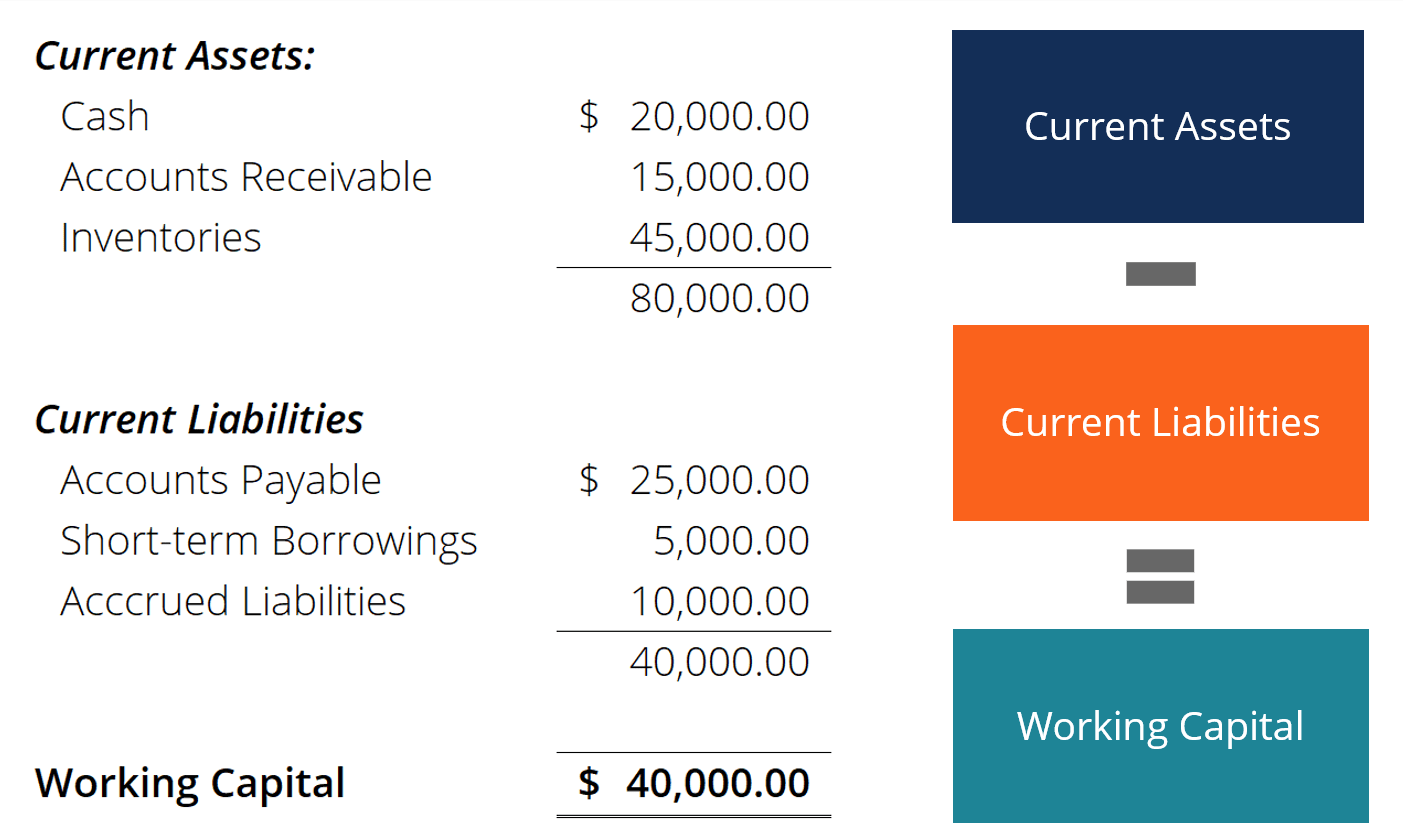
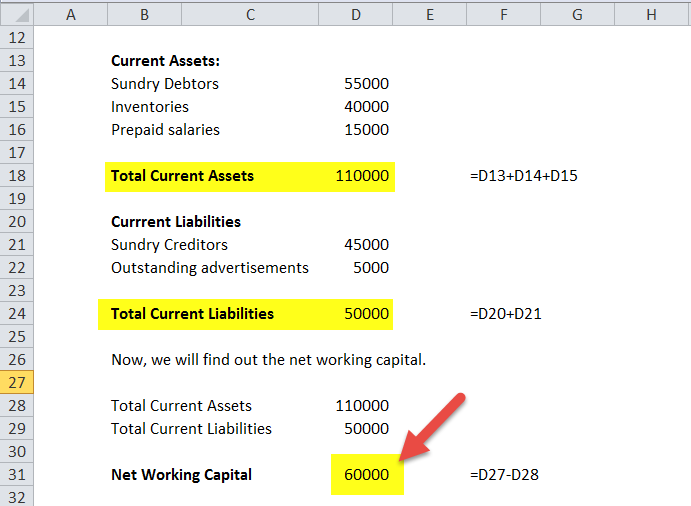
You can find it by taking your current assets and subtracting your current liabilities, both of which can be found on your balance sheet. Setting up a net working capital schedule step 1. This may indicate that the company is in stock too much or has not invested surplus cash.
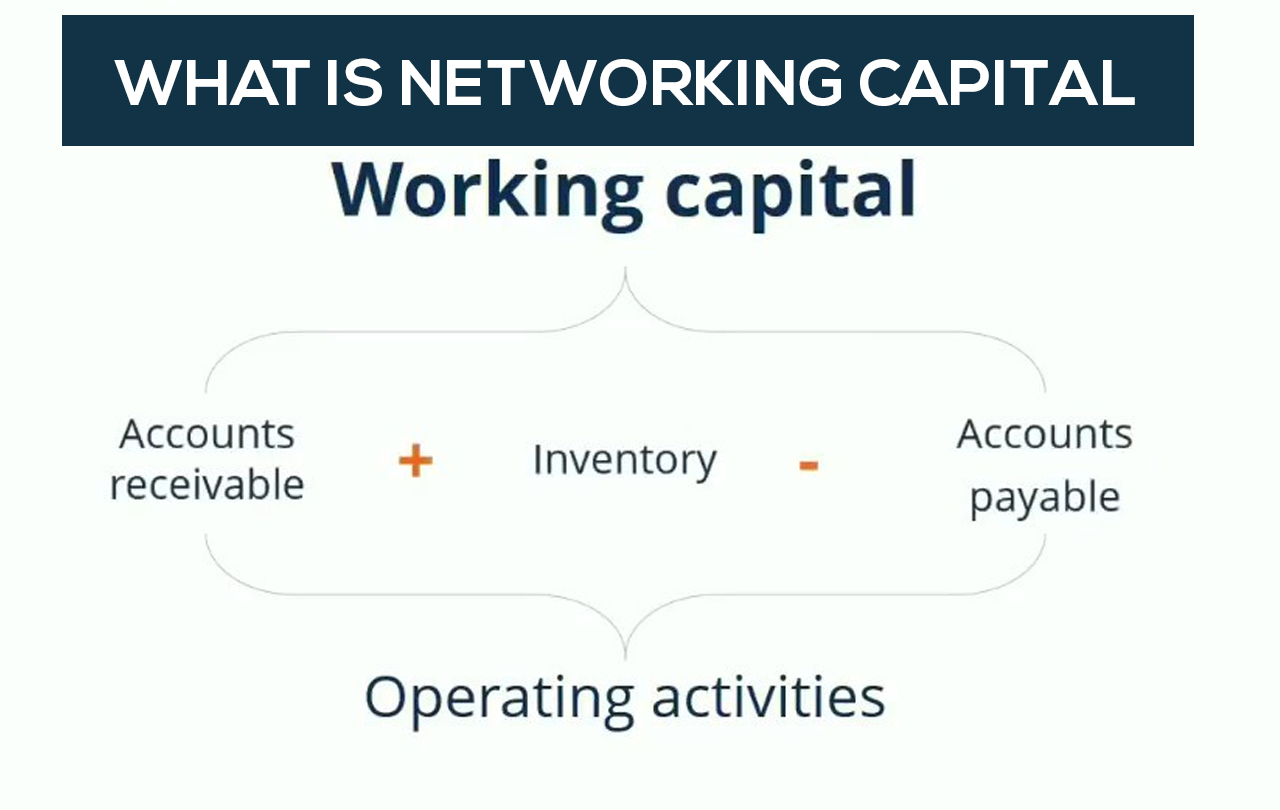
The net working capital ratio’s numerator and denominator come from a business’s balance sheet, and you can find them in the formula below: Current assets minus current liabilities. If a business has $1,000 in cash, $2,000 in accounts receivables, $2,000 in inventory, and $2,500 in current liabilities, what is its net working.





![Working Capital Formula and Calculation Exercise [Excel Template]](https://wsp-blog-images.s3.amazonaws.com/uploads/2018/01/18162010/wc1-900x663.gif)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_What_Changes_in_Working_Capital_Impact_Cash_Flow_Sep_2020-01-13de858aa25b4c5389427b3f49bef9bc.jpg)